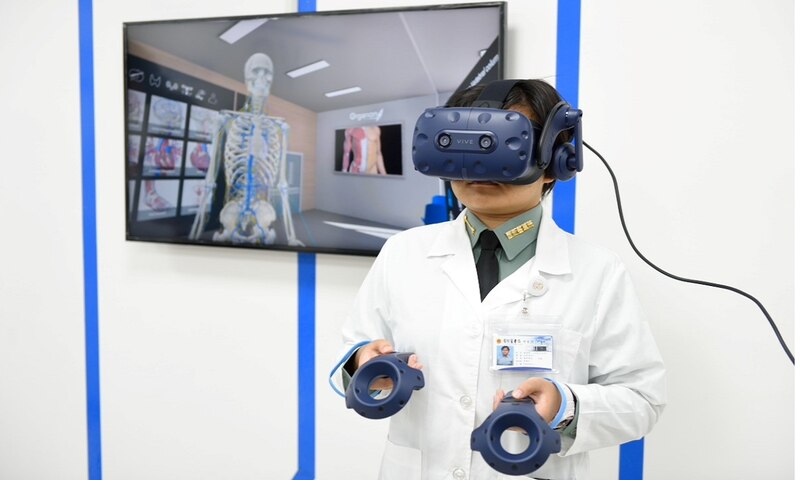
Taiwan NDMC Collaborates With HTC DeepQ To Build The Largest Mixed Reality Anatomy Classroom In Taiwan
Lin Greta / 2019.12.6
Taiwan National Defense Medical Center (NDMC) partners with DeepQ, a healthcare division of technology innovator HTC, to build the largest Mixed Reality (MR) anatomy classroom in Taiwan. MR combines Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) so users can switch between real and virtual anatomy classroom environments, choosing the appropriate learning method according to education situations.
With President of National Defense Medical Center, Tai-Lung Cha’s fully support, professor Guo-Xing Ma, Director of Research and Development at the National Defense Medical Center, leads the team at the Graduate Institue of Biology and Anatomy to review the Chinese content of the VR anatomy application, and develop innovative anatomical teaching methods.
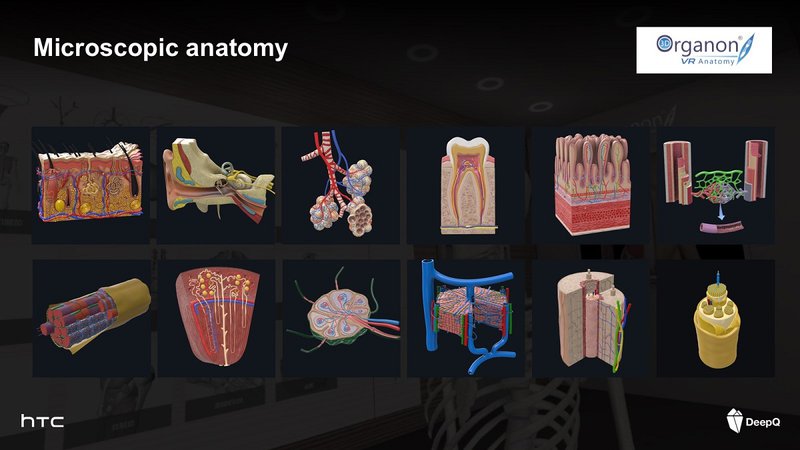
Wearing HTC VIVE Pro, students of the National Defense Medical Center can see thousands of interactive human body models in a 3D Organon MR anatomy education application. Through interacting with the simulation, the three-dimensional spatial relationship of the human body model can be comprehensively understood from various directions. The model allows students to learn about the movements of joints and muscles and even the beating of the heart. It is also possible to learn microscopic anatomy, which is usually difficult to understand, such as intestinal villi, chyle ducts, muscle fibers, glomerulus and etc., breaking the learning bottleneck from the past.
In addition to immersive self-learning, students can also use the world’s most advanced VR anatomy test to practice for the USMLE (United States Medical Licensing Examination). In the labolatory class, students and teachers can switch quickly between VR and the real world with one click, placing the virtual human body next to the real cadavers, in the meantime using the anatomy atlas to learn more in a very efficient way.
President of National Defense Medical Center, Tai-Lung Cha pointed out: “Anatomy is the most important cornerstone of medicine. However, it was very difficult to learn the special relationship of the human anatomy in the past. Not to mention the transition of the knowledge to interact with patients in the future. The learning method of MR compares between a virtual and real cadaver, which helps students to understand the corresponding structures in real patients, significantly improving the clinical skills.”
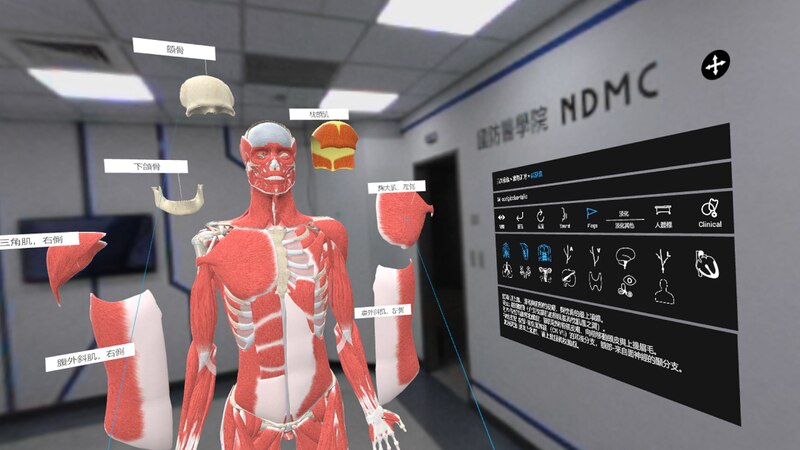

The president of HTC DeepQ, Edward Chang, said: “The learning method of MR can release teachers’ imagination and provide them key tools for education, so that students and teachers can have more bonding interaction. As soon as teachers in class switch the environment function, the virtual space can immediately fuse to the real environment. It overcomes the disadvantage of VR that cannot interact with students directly and cannot observe their understanding of the course from the teaching interaction. It makes learning anatomy more interesting and efficient. The MR technology, combining the advantages of VR and AR, will also have breakthrough applications in other professional fields.”
National Defense Medical Center and HTC DeepQ are developing a new generation of anatomy VR learning materials in the future so that students can leverage the technology for self-learning. The learning contents can be modified according to the students’ test results in the assessment of VR anatomy, in order to teach students in accordance with their aptitude and create personalized and accurate teaching materials. Experiences of anatomy education are scheduled to be shared at the international conference next year.